Introduction to AWS (American Welding Society)
The American Welding Society (AWS) is a non-profit organization that was established in 1919 with the mission to advance the science, technology, and application of welding and allied joining and cutting processes. Over the years, AWS has grown to become a leading authority in the welding industry, providing a wealth of resources, including certifications, standards, conferences, and publications that promote welding excellence.

The Importance of AWS Welding Codes
AWS welding codes are critical guidelines that ensure the quality, safety, and reliability of welding practices across various industries. These codes serve as a standardized set of procedures and criteria that welders, inspectors, and engineers must adhere to, ensuring that welded structures and components meet stringent quality and safety standards. By following AWS welding codes, professionals in the welding industry can achieve consistent and high-quality results, minimize risks, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Purpose of the Article
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive overview of AWS welding codes, including their significance, common types, certification processes, technical requirements, and real-world applications. By understanding these codes, readers can appreciate the role they play in enhancing welding practices and ensuring the integrity of welded structures.
Overview of AWS Welding Codes
Definition of AWS Welding Codes
AWS welding codes are a set of guidelines and standards developed by the American Welding Society to ensure the quality, safety, and consistency of welding practices. These codes cover a wide range of welding processes, materials, and applications, providing detailed specifications for the procedures, qualifications, and inspection methods that must be followed. The primary goal of these codes is to promote best practices in welding, reduce the risk of defects, and ensure the structural integrity of welded components.
Common AWS Welding Codes
There are several AWS welding codes, each tailored to specific materials and applications. Some of the most widely used codes include:
- AWS D1.1: Structural Welding Code – Steel
The AWS D1.1 code is one of the most widely recognized and utilized welding standards in the industry. It covers the welding requirements for structural steel, including the design, fabrication, and inspection of welded steel structures. This code is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of steel constructions such as buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- AWS D1.3: Structural Welding Code – Sheet Steel
The AWS D1.3 code focuses on the welding of sheet steel, typically used in applications where thin steel materials are employed. This code outlines the procedures and requirements for welding sheet steel to ensure proper joint strength and quality, which is crucial in industries such as automotive manufacturing and light structural applications.
- AWS D1.6: Structural Welding Code – Stainless Steel
The AWS D1.6 code addresses the welding of stainless steel, a material known for its corrosion resistance and strength. This code provides guidelines for the design, welding procedures, and inspection of stainless steel structures. It is particularly important in industries where stainless steel is used for its durability and resistance to harsh environments, such as chemical processing, food and beverage production, and medical equipment manufacturing.
Certification Process for AWS Welding Codes
Steps to Achieve Certification
- Preparation and Training:
The first step in achieving AWS certification involves thorough preparation and training. Aspiring welders must enroll in training programs that cover the theoretical and practical aspects of welding. These programs are designed to teach students the essential skills and knowledge required to meet AWS standards.
- Theoretical Examination:
Candidates must pass a written examination that tests their understanding of welding principles, codes, and safety practices. This exam ensures that they have the necessary theoretical foundation to apply welding codes effectively.
- Practical Examination:
In addition to the theoretical exam, candidates must demonstrate their welding skills through a practical test. This involves performing specific welding tasks under the supervision of a certified inspector. The practical exam assesses the candidate’s ability to produce high-quality welds that meet AWS standards.
- Inspection and Evaluation:
The final step in the certification process is the inspection and evaluation of the candidate’s work. Certified inspectors review the welds for adherence to AWS codes and standards, checking for defects and ensuring the overall quality of the work. Successful candidates are awarded AWS certification, recognizing their proficiency in welding according to AWS guidelines.
Benefits of AWS Certification
- For Welders:
AWS certification is a prestigious credential that enhances a welder’s career prospects. Certified welders are recognized for their expertise and commitment to quality, making them more competitive in the job market. Certification also provides opportunities for career advancement and higher earning potential.
- For Contractors and Projects:
For contractors and project managers, employing AWS-certified welders ensures that welding work is performed to the highest standards of quality and safety. This reduces the risk of structural failures and costly repairs, enhances the credibility of the contractor, and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. Overall, AWS certification contributes to the success and reliability of construction and manufacturing projects.
Latest Updates in AWS Welding Codes
Recent Changes and Updates
- Updates to Standards and Procedures:
The AWS continuously reviews and updates its welding codes to reflect advances in technology, materials, and industry practices. Recent updates might include changes to welding parameters, new welding techniques, and revisions to quality control procedures to enhance safety and efficiency. For instance, advancements in automation and robotics in welding may lead to new standards for integrating these technologies into welding processes.
- Impact on the Industry:
These updates ensure that the welding industry remains current with technological advancements and maintains high standards of quality and safety. They also address emerging challenges and opportunities, such as the increased use of advanced materials and the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental considerations in manufacturing processes.
Applications of the Latest Updates
- Adapting to New Technologies:
Welding professionals must stay informed about the latest updates to AWS codes to effectively incorporate new technologies into their work. This includes understanding how to use advanced welding equipment, implementing updated safety practices, and applying new welding techniques. Continuous education and training are essential for keeping skills current and ensuring compliance with the latest standards.
- Case Studies and Real-World Examples:
Highlighting specific projects that have successfully implemented the latest AWS code updates can provide valuable insights. For example, a case study might focus on a bridge construction project that utilized new welding techniques and materials specified in the updated AWS D1.1 code. These real-world examples demonstrate the practical benefits of adhering to updated codes, such as improved structural integrity, reduced construction time, and cost savings.
Real-World Applications of AWS Welding Codes in Construction Projects

Examples of Projects Utilizing AWS Welding Codes
- High-Rise Buildings:
AWS welding codes are crucial in the construction of high-rise buildings, where the integrity and strength of steel frameworks are paramount. These codes ensure that the welds used in connecting structural steel components meet the required safety and quality standards. For instance, the AWS D1.1 code is commonly applied in the welding of beams, columns, and other structural elements in skyscrapers.
- Bridges and Infrastructure:
Bridges and other critical infrastructure projects often rely on AWS welding codes to guarantee the durability and safety of welded joints. By adhering to codes such as AWS D1.1, engineers and welders can ensure that the welded connections in bridges can withstand the stresses and loads they will encounter over their lifespan. This results in safer and more reliable transportation networks.
- Industrial Facilities:
In the construction of industrial facilities, including factories, refineries, and power plants, AWS welding codes ensure that the welding processes used in constructing pressure vessels, pipelines, and structural supports meet stringent safety and quality criteria. For example, AWS D1.6 may be applied in the welding of stainless steel components in chemical processing plants, ensuring resistance to corrosion and high temperatures.
Challenges and Solutions in Compliance with AWS Welding Codes
- Common Challenges:
- Technical Complexity: Understanding and implementing AWS welding codes can be technically challenging due to the detailed specifications and strict requirements. Welders and inspectors must be thoroughly trained and knowledgeable about the codes to ensure compliance.
- Resource Constraints: Ensuring compliance with AWS codes can be resource-intensive, requiring investment in proper training, equipment, and inspection processes. Smaller contractors may face difficulties in allocating the necessary resources.
- Solutions and Best Practices:
- Comprehensive Training: Providing comprehensive training programs for welders, inspectors, and engineers is essential for overcoming technical complexity. Regular workshops, certifications, and on-the-job training can help ensure that all personnel are up-to-date with the latest AWS standards and practices.
- Investment in Quality Equipment: Investing in high-quality welding equipment and inspection tools is crucial for maintaining compliance with AWS codes. Modern welding technologies and advanced non-destructive testing (NDT) methods can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of welding processes and inspections.
- Effective Quality Control Systems: Implementing robust quality control systems and procedures helps ensure that all welding activities adhere to AWS standards. This includes maintaining detailed records, conducting regular inspections, and addressing any issues promptly to prevent defects and ensure the longevity of welded structures.
Training and Skill Development for AWS Welding Codes
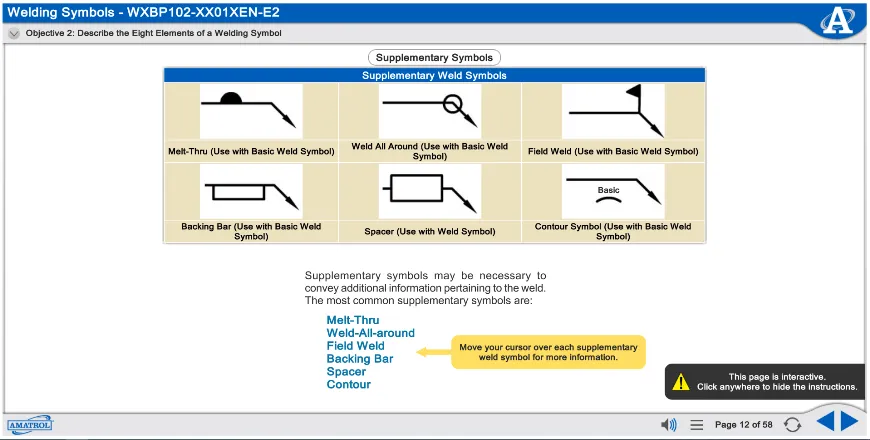
Training Programs and Learning Resources
- Formal Training Programs:
Many institutions and organizations offer formal training programs specifically designed to teach welders about AWS welding codes. These programs often include a combination of classroom instruction and hands-on practice, covering topics such as welding theory, safety practices, and the specifics of various AWS codes. Completing these programs helps ensure that welders have a comprehensive understanding of the standards they need to follow.
- Online Courses and Tutorials:
With the rise of digital learning, numerous online courses and tutorials are available for those looking to study AWS welding codes. These resources offer flexible learning options, allowing welders to study at their own pace. Online platforms often provide interactive modules, video demonstrations, and quizzes to reinforce learning.
- Reference Materials and Guides:
AWS provides a wealth of reference materials and guides, including codebooks, manuals, and technical papers. These resources are invaluable for welders seeking to deepen their understanding of specific codes and stay current with the latest updates. Access to these materials ensures that welders have reliable information to reference in their daily work.
Advice for Beginners in Welding
- Start with the Basics:
Beginners should start by building a strong foundation in welding fundamentals. This includes understanding basic welding techniques, safety protocols, and the types of materials commonly used in welding. Mastering the basics provides a solid platform for learning more advanced skills and codes.
- Seek Certification Early:
Obtaining AWS certification early in one’s career can be highly beneficial. Certification demonstrates a commitment to quality and adherence to industry standards, making certified welders more attractive to employers. It also provides a sense of accomplishment and confidence in one’s skills.
- Practice Consistently:
Regular practice is essential for developing proficiency in welding. Beginners should take every opportunity to practice different welding techniques and work with various materials. Hands-on experience is crucial for reinforcing theoretical knowledge and improving practical skills.
Comparison of AWS Welding Codes with International Standards
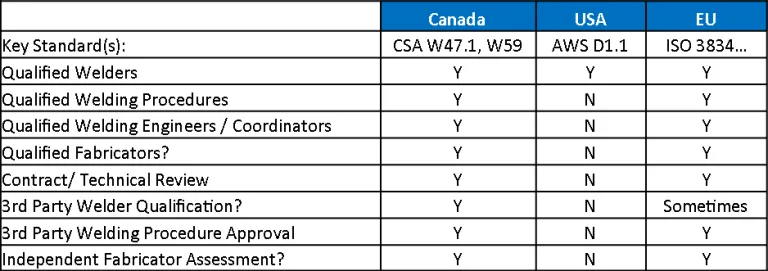
Comparison with ISO Standards
- Similarities: Both AWS and ISO (International Organization for Standardization) welding standards aim to ensure the quality, safety, and reliability of welded structures. They provide comprehensive guidelines for welding procedures, qualifications, and inspections. Many of the fundamental principles, such as the importance of proper joint design, the use of appropriate welding parameters, and the necessity of rigorous testing and inspection, are common to both AWS and ISO standards.
- Differences: While AWS standards are primarily used in the United States, ISO standards are internationally recognized and adopted by many countries. ISO standards tend to be more general and may require adaptation to specific national or regional requirements. AWS standards, on the other hand, are often more detailed and tailored to specific applications and industries in the U.S. For example, AWS D1.1 provides extensive guidelines for structural steel welding, whereas ISO 3834 focuses on the quality requirements for fusion welding of metallic materials.
- Adoption and Integration: Many multinational companies and projects integrate both AWS and ISO standards to meet diverse regulatory and client requirements. This dual compliance can ensure that welding practices adhere to the highest international standards, facilitating global operations and exports.
Comparison with European EN Standards
- Similarities: European Norms (EN) standards, like AWS and ISO standards, are designed to ensure the quality and safety of welding practices. They cover a wide range of materials and welding processes and include detailed specifications for welding procedures, welder qualifications, and inspections. EN standards also emphasize the importance of non-destructive testing and quality control.
- Differences: EN standards are developed by the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) and are widely used across Europe. They are often aligned with ISO standards to facilitate international trade and regulatory compliance. However, there can be differences in specific requirements and terminology. For instance, EN 1090 focuses on the execution of steel structures and aluminum structures, with detailed requirements for welding, whereas AWS D1.2 deals specifically with the welding of aluminum.
- Harmonization Efforts: There have been ongoing efforts to harmonize AWS, ISO, and EN standards to streamline international welding practices and reduce barriers to trade. This harmonization helps ensure that welded products can meet the requirements of multiple standards, facilitating their acceptance in different markets.
Applications and Effectiveness of Compliance with Multiple Standards
- Practical Applications: Compliance with multiple standards is common in large-scale international projects, such as offshore oil and gas platforms, where structures must meet the stringent requirements of various regulatory bodies. For example, a project might adhere to AWS D1.1 for structural steel welding while also complying with ISO 9001 for quality management systems and EN 1090 for execution of steel structures.
- Benefits of Multi-Standard Compliance:
- Enhanced Quality and Safety: Adhering to multiple standards can lead to higher quality and safer welding practices by incorporating the best practices and requirements from each standard.
- Global Market Access: Compliance with international standards like ISO and EN, in addition to AWS standards, can facilitate market access and acceptance of welded products in different countries.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that demonstrate the ability to meet multiple standards can differentiate themselves in the market, showcasing their commitment to excellence and regulatory compliance.
Common Issues and Solutions in Adhering to AWS Welding Codes
Common Issues
- Technical Errors: One of the most frequent issues in adhering to AWS welding codes is technical errors. These errors can occur due to improper joint design, incorrect welding parameters, or inadequate preheat and interpass temperature control. Technical errors can lead to defects such as cracks, porosity, and incomplete fusion, which compromise the integrity of the weld.
- Lack of Proper Training: Without proper training, welders may lack the necessary skills and knowledge to follow AWS codes accurately. This can result in substandard welds that fail to meet quality and safety standards. Additionally, untrained inspectors may not correctly identify defects or ensure compliance during inspections.
- Inadequate Quality Control: Inadequate quality control processes can lead to inconsistent welding practices and overlooked defects. This can happen due to insufficient documentation, lack of standardized procedures, or failure to conduct regular inspections and tests. Poor quality control increases the risk of structural failures and costly repairs.
Solutions and Best Practices
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Investing in comprehensive training programs for welders, inspectors, and engineers is essential. These programs should cover the theoretical and practical aspects of AWS welding codes, ensuring that all personnel are well-versed in the standards. Regular refresher courses and certifications can help maintain high levels of proficiency.
- Standardized Procedures and Documentation: Implementing standardized welding procedures and thorough documentation practices can significantly improve adherence to AWS codes. Detailed Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) and Procedure Qualification Records (PQR) should be maintained and followed strictly. Proper documentation ensures traceability and accountability in welding activities.
- Advanced Inspection and Testing Methods: Utilizing advanced non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as radiographic (X-ray) and ultrasonic testing, can enhance the detection of internal defects. Regular visual inspections by certified inspectors should also be conducted to identify surface defects. Combining these inspection methods ensures comprehensive quality control.
- Quality Control Systems: Implementing robust quality control systems and processes is crucial. This includes setting up regular inspection schedules, maintaining detailed records of welding activities, and promptly addressing any issues that arise. Effective quality control systems help prevent defects and ensure consistent compliance with AWS standards.
- Continuous Improvement: Emphasizing continuous improvement in welding practices can help address common issues. Encouraging feedback from welders and inspectors, conducting regular audits, and staying updated with the latest advancements in welding technology and standards can drive ongoing enhancements in quality and compliance.
Conclusion
AWS welding codes are indispensable to the welding industry, ensuring that welding practices adhere to the highest standards of quality and safety. By providing comprehensive guidelines for welding procedures, welder qualifications, and inspection methods, these codes help prevent defects, ensure structural integrity, and promote the reliability of welded structures across various industries. Adherence to AWS codes not only enhances the performance and longevity of welded components but also contributes to the overall safety and efficiency of construction and manufacturing projects.
Leave a Reply